What name should I give my mantid? Julia or Julian? First you need to know the sex of the animal.
I think it is not only interesting to know the sex of your mantis for naming purposes. Anyone planning to breed with their mantids should know whether they have the necessary ingredients.
Mantises reproduce sexually. There are only very few exceptions that are able to reproduce via parthenogenesis. However, as we know from some phasmid species, only female larvae hatch from these. Therefore f nly all mantid species exhibit sexual dimorphism (sex-specific differences).
Of course, you could also simply wait until they reach sexual maturity and then see what comes out. However, in many mantid species the males reach sexual maturity 2-3 moults before the females. It is not only the different maturation time until the adult moult, but the females then need even longer until they are ready to mate. It is therefore advantageous to recognize the sex differences at an early stage in order to keep the male mantids at the lower temperature limit and the female praying mantises at the upper limit to compensate for this time lag. However, please take care not to mate males and females of the same parents too often in order to avoid the risk of genetic defects.
Sex determination in adult praying mantises
Even with adult praying mantises, you first need to know and recognize the differences between the sexes. Since the male mantids become adults more quickly and also require fewer moults, we have a first clue, the size. Female mantids are generally larger and stronger. The overall appearance of males is rather small and thin in comparison.

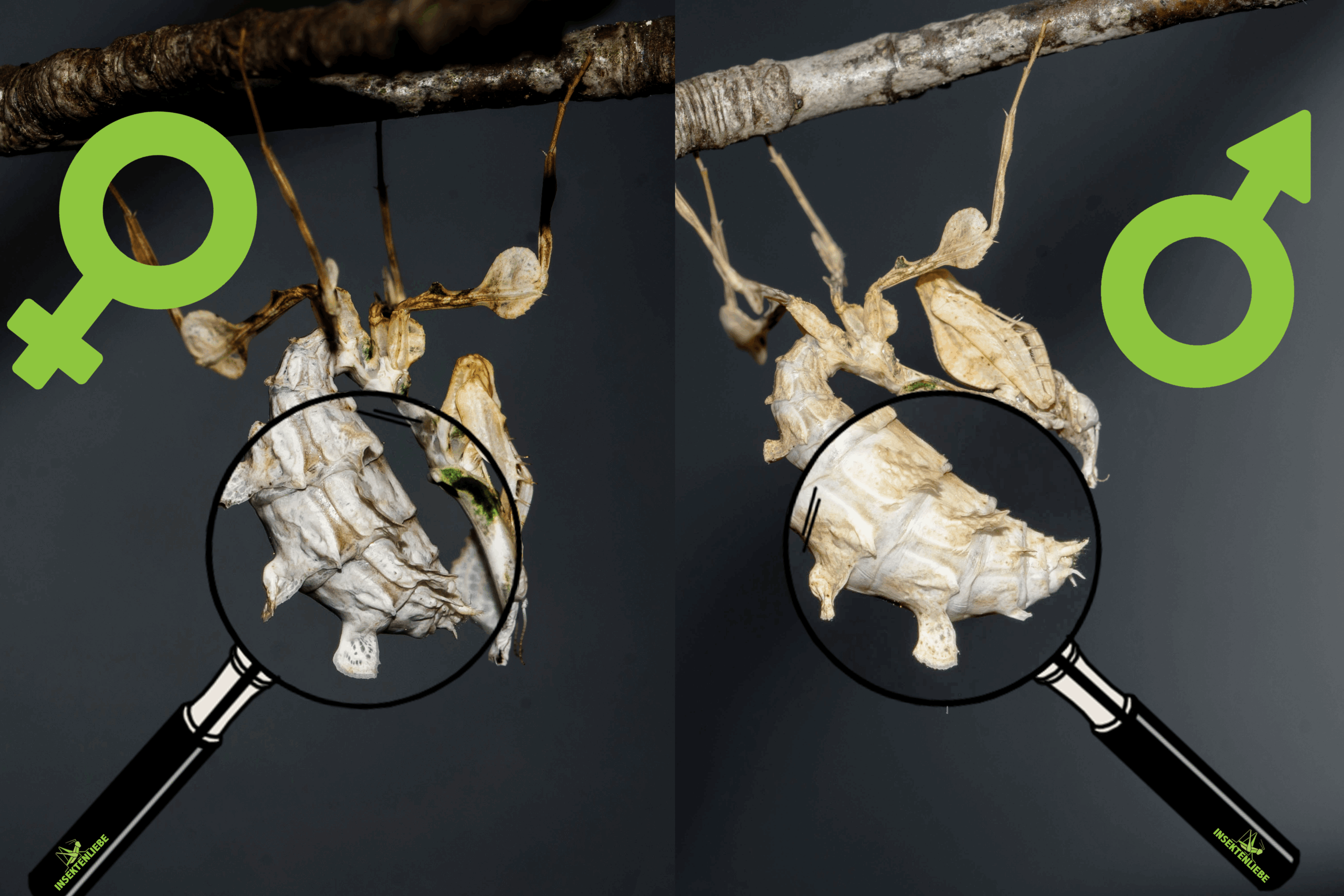
The visible number of segments on the abdomen is 8 in males and only 6 in females.
The wings of the males extend far beyond the abdomen and due to the size of the wings and the shape of the body, most are good and agile fliers. In females, the wings usually end at the tip of the abdomen. If they try to fly at all, it is more like a dive than locomotion.
The antennae of male mantids are longer and sometimes thickened. There are sensory cells in the antennae or antennae. This enables the males to better pick up mechanical stimuli (feel) and chemical stimuli (smell). As soon as a male picks up the pheromones via his antennae and is sexually mature, he will follow the scent trail. In this way, the roaming males find the females, which are usually relatively slow-moving, even over long distances .
Sex determination in juvenile praying mantises
Logically, one could now assume that if the males grow up faster, they will also grow faster and this could be an indication. However, the Moult intervals are approximately the same with the same parameters. However, the males molt 2-3 times less than the females and do not gain as much size during the molts from L3-L4.
In all mantid species, males can be distinguished from females by the number of visible sternites (abdominal segments). A trained eye can differentiate with or without a magnifying glass from L3 onwards on the basis of the segments. The subgenital plate is always the most reliable.The subgenital plate is the plate below the genitalia. One large segment at the tip is always a female, two smaller segments at the tip a male. At the beginning it is difficult to tell the difference. It often helps to photograph the underside of the abdomen and enlarge the plate. After your first experiences, you will slowly but surely get an eye for it and will soon no longer need magnification.

Sex determination of species-specific praying mantises
Additional sexual characteristics in Hymenopus coronatus:
There are several additional ways to recognize the sex of orchid mantis. First of all, you can tell the sex by the color of the neck band. A brown nuchal band indicates a male and a green one a female. The coloration of the males can sometimes go slightly greenish, but never becomes as green as in females. However, this cannot be recognized in the earlier larval stages, at least not easily. And when the time comes, it is just as easy to differentiate according to other characteristics such as abdomen, body size and lobes.
The female H. coronatus have large, leaf-shaped lobes which can be used as a further indication of sex determination.
The abdomen of the male orchid mantis is oval and has 6 segments and the female abdomen has a round shape and 5 sternites.

Additional sexual characteristics in Blepharopsis mendica, Idolomantis diabolica, Gongylodes gongylodes:
The males have thickened antennae in the subadult and adult stages.
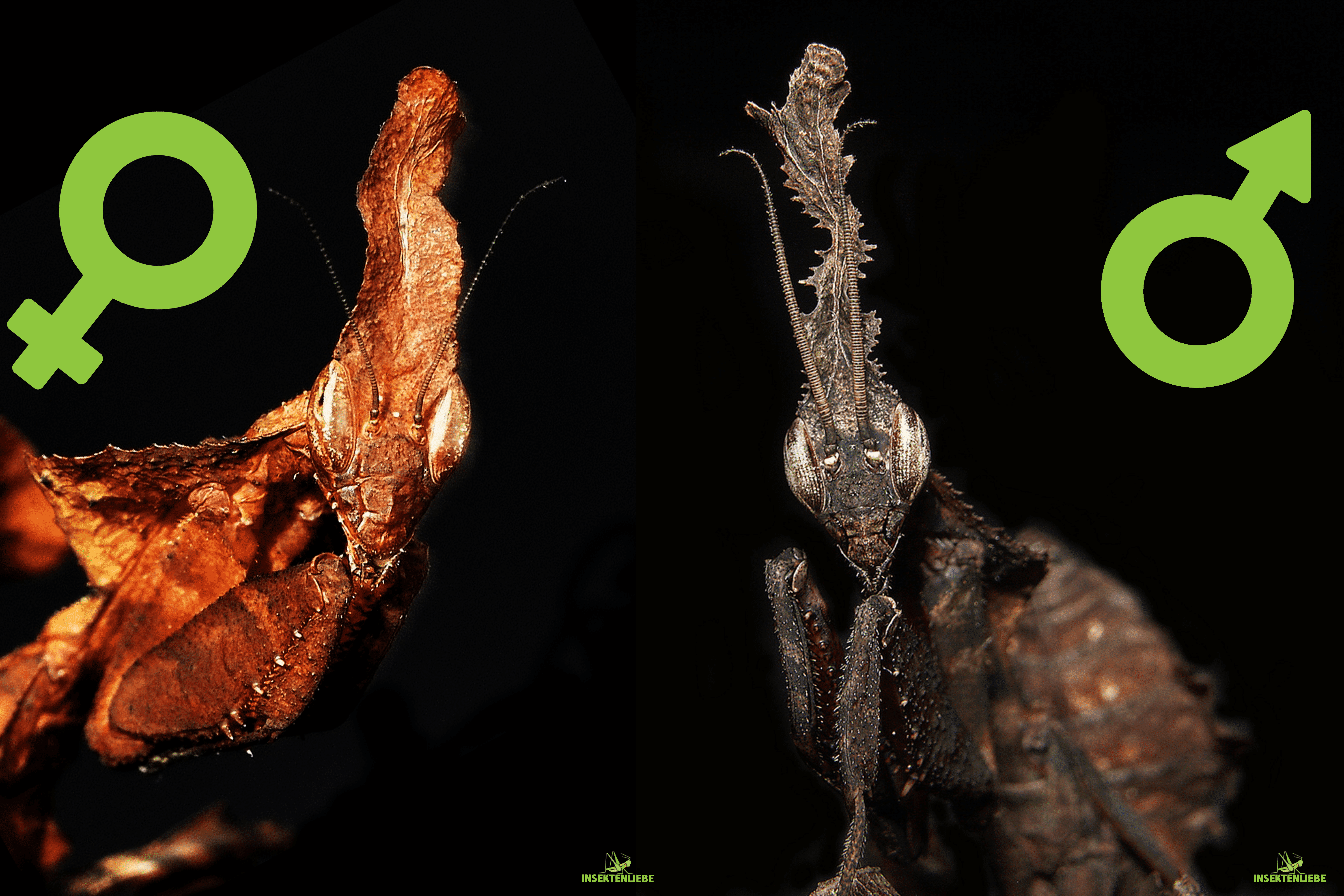
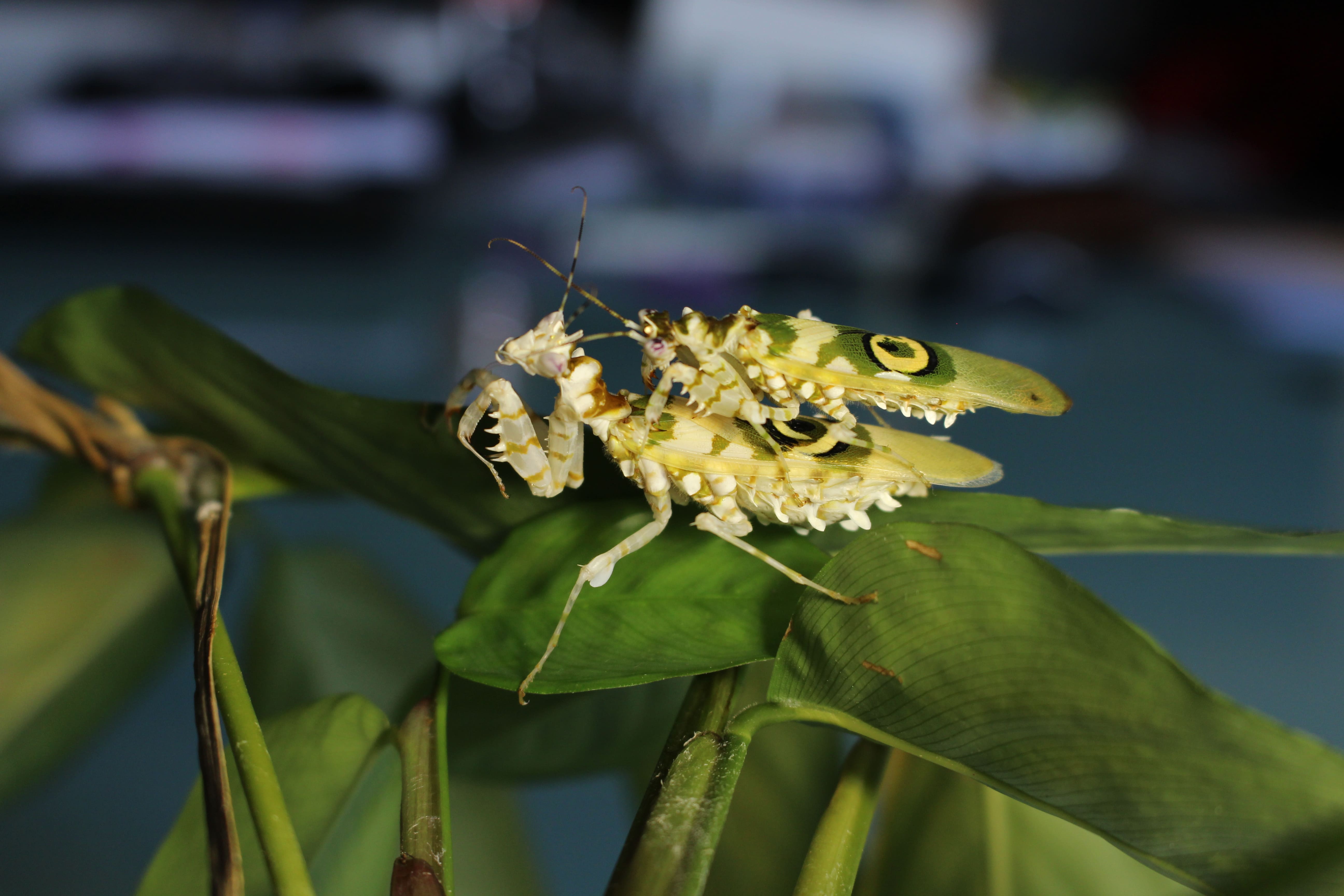
Additional sexual characteristics in Idolomantis diabolica, Gongylus gongylodes, Blepharopsis mendica and Pseudocreobotra wahlbergii:
From L3 onwards, male mantids have an additional spine on the abdomen.


Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.